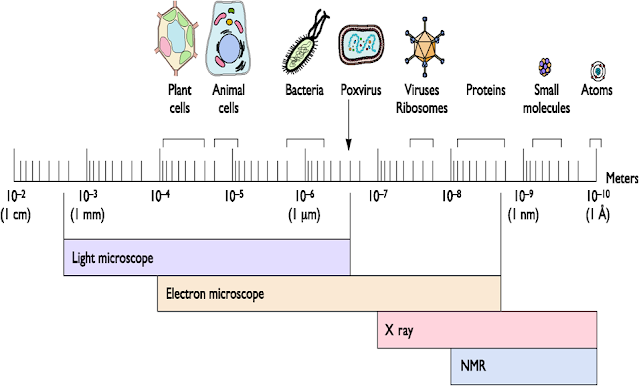
A virus is an obligate intracellular parasite containing genetic material surrounded by a protein Virus particles can only be observed by an electron microscope
Viral Properties
- Inert (nucleoprotein ) filterable Agents
- Obligate intracellular parasites
- Cannot make energy or proteins independent of a host cell
- Genome is RNA or DNA but not both.
- Have a naked capsid or envelope with attached proteins
- Multiply by a complex process, not by binary fission.
- Non-living entities??
Terms & Definitions in Virology
- Capsid: The protein shell, or coat, that encloses the NA genome.
- Capsomeres: Morphologic units of Capsid. Capsomeres represent clusters of polypeptides
- Defective virus: A virus particle that is functionally deficient in some aspect of replication.
- Envelope: A lipid-containing membrane that surrounds some virus particles. It is acquired during viral maturation by a budding process through a cellular membrane.
- Peplomers: virus-encoded glycoproteins are exposed on the surface of the envelope.
- Nucleocapsid: The protein-nucleic acid complex representing the packaged form of the viral genome.
- Virion: The complete virus particle. In some instances (eg, papillomaviruses, picornaviruses), the virion is identical with the nucleocapsid. In more complex virions (herpesviruses, orthomyxoviruses), this includes the nucleocapsid plus a surrounding envelope. This structure, the virion, serves to transfer the viral nucleic acid from one cell to another.
The size of viruses